Fast Marching on 3D Meshes
本文共 14630 字,大约阅读时间需要 48 分钟。
3D mesh的fast marching 跟2D图片的fast marching类似.
2D图片是规则的平面网格,点的 ux,uy 是通过上或下,左或右(具体哪个,是通过距离小的点去确定),具体请参考 而3D mesh上点的 ux,uy 是通过与它位于同一个三角形的其他两个点去确定在本例中,W(也就是weight)全为1,这里可以理解为流速F
u为距离D,即我们要求的 Δx , Δy 分别为点到它两个父节点的距离 这样,根据2D情况中的公式就可以求出每个点的距离了,最终求出D 下面给出关于求D的关键代码/*------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/// Name : GW_GeodesicMesh::PerformFastMarchingOneStep/** * \return [GW_Bool] Is the marching process finished ? * \author Gabriel Peyr� * \date 4-13-2003 * * Just one update step of the marching algorithm. *//*------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/GW_INLINEGW_Bool GW_GeodesicMesh::PerformFastMarchingOneStep(){ if( ActiveVertex_.empty() ) return GW_True; GW_ASSERT( bIsMarchingBegin_ );// std::make_heap( ActiveVertex_.begin(), ActiveVertex_.end(), GW_GeodesicVertex::CompareVertex ); GW_GeodesicVertex* pCurVert = ActiveVertex_.front(); GW_ASSERT( pCurVert!=NULL ); std::pop_heap( ActiveVertex_.begin(), ActiveVertex_.end(), GW_GeodesicVertex::CompareVertex ); ActiveVertex_.pop_back(); pCurVert->SetState( GW_GeodesicVertex::kDead ); if( NewDeadVertexCallback_!=NULL ) NewDeadVertexCallback_( *pCurVert );#if 0 // just for debug for( IT_GeodesicVertexVector it = ActiveVertex_.begin(); it!=ActiveVertex_.end(); ++it ) GW_ASSERT( pCurVert->GetDistance()<=(*it)->GetDistance() );#endif for( GW_VertexIterator VertIt = pCurVert->BeginVertexIterator(); VertIt!=pCurVert->EndVertexIterator(); ++VertIt ) { GW_GeodesicVertex* pNewVert = (GW_GeodesicVertex*) *VertIt; GW_ASSERT( pNewVert!=NULL ); /* compute it's new value */ if( pCurVert->GetIsStoppingVertex() && !pNewVert->GetIsStoppingVertex() && pNewVert->GetState()==GW_GeodesicVertex::kFar ) { // this vertex is not allowed to add alive vertex that are not stopping. } else { /* compute it's new distance using neighborhood information */ GW_Float rNewDistance = GW_INFINITE; for( GW_FaceIterator FaceIt=pNewVert->BeginFaceIterator(); FaceIt!=pNewVert->EndFaceIterator(); ++FaceIt ) //该循环找出与点距离最近两个父节点,因为点不是按mesh的边走,可以穿过边到达,那么穿过边的两个端点即为该点的两个父节点 { GW_GeodesicFace* pFace = (GW_GeodesicFace*) *FaceIt; GW_ASSERT( pFace!=NULL ); GW_GeodesicVertex* pVert1 = (GW_GeodesicVertex*) pFace->GetNextVertex( *pNewVert ); GW_ASSERT( pVert1!=NULL ); GW_GeodesicVertex* pVert2 = (GW_GeodesicVertex*) pFace->GetNextVertex( *pVert1 ); GW_ASSERT( pVert2!=NULL ); if( pVert1->GetDistance()> pVert2->GetDistance() ) { GW_GeodesicVertex* pTempVert = pVert1; pVert1 = pVert2; pVert2 = pTempVert; } rNewDistance = GW_MIN( rNewDistance, this->ComputeVertexDistance( *pFace, *pNewVert, *pVert1, *pVert2, *pCurVert->GetFront() ) ); } switch( pNewVert->GetState() ) { case GW_GeodesicVertex::kFar: /* ask to the callback if we should update this vertex and add it to the path */ if( VertexInsersionCallback_==NULL || VertexInsersionCallback_( *pNewVert,rNewDistance ) ) { pNewVert->SetDistance( rNewDistance ); /* add the vertex to the heap */ ActiveVertex_.push_back( pNewVert ); std::push_heap( ActiveVertex_.begin(), ActiveVertex_.end(), GW_GeodesicVertex::CompareVertex ); /* this one can be added to the heap */ pNewVert->SetState( GW_GeodesicVertex::kAlive ); pNewVert->SetFront( pCurVert->GetFront() ); } break; case GW_GeodesicVertex::kAlive: /* just update it's value */ if( rNewDistance<=pNewVert->GetDistance() ) { /* possible overlap with old value */ if( pCurVert->GetFront()!=pNewVert->GetFront() ) pNewVert->GetFrontOverlapInfo().RecordOverlap( *pNewVert->GetFront(), pNewVert->GetDistance() ); pNewVert->SetDistance( rNewDistance ); pNewVert->SetFront( pCurVert->GetFront() ); // hum, check if we can correct this (avoid recomputing the whole heap). std::make_heap( ActiveVertex_.begin(), ActiveVertex_.end(), GW_GeodesicVertex::CompareVertex ); } else { /* possible overlap with new value */ if( pCurVert->GetFront()!=pNewVert->GetFront() ) pNewVert->GetFrontOverlapInfo().RecordOverlap( *pCurVert->GetFront(), rNewDistance ); } break; case GW_GeodesicVertex::kDead: /* inform the user if there is an overlap */ if( pCurVert->GetFront()!=pNewVert->GetFront() ) pNewVert->GetFrontOverlapInfo().RecordOverlap( *pCurVert->GetFront(), rNewDistance ); break; default: GW_ASSERT( GW_False ); } } } /* have we finished ? */ bIsMarchingEnd_ = ActiveVertex_.empty(); /* the user can force ending of the algorithm */ if( ForceStopCallback_!=NULL && bIsMarchingEnd_==GW_False ) bIsMarchingEnd_ = ForceStopCallback_(*pCurVert); return bIsMarchingEnd_;} /*------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/// Name : GW_GeodesicMesh::ComputeVertexDistance/*** \param CurrentVertex [GW_GeodesicVertex&] The vertex to update.* \param Vert1 [GW_GeodesicVertex&] It's 1st neighbor.* \param Vert2 [GW_GeodesicVertex&] 2nd vertex.* \return The value of the distance according to this triangle contribution.* \author Gabriel Peyr�* \date 4-12-2003* * Compute the update of a vertex from inside of a triangle.*//*------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/GW_INLINEGW_Float GW_GeodesicMesh::ComputeVertexDistance( GW_GeodesicFace& CurrentFace, GW_GeodesicVertex& CurrentVertex, GW_GeodesicVertex& Vert1, GW_GeodesicVertex& Vert2, GW_GeodesicVertex& CurrentFront ){ GW_Float F = this->WeightCallback_( CurrentVertex ); if( Vert1.GetState()!=GW_GeodesicVertex::kFar || Vert2.GetState()!=GW_GeodesicVertex::kFar ) { GW_Vector3D Edge1 = Vert1.GetPosition() - CurrentVertex.GetPosition(); GW_Float b = Edge1.Norm(); Edge1 /= b; GW_Vector3D Edge2 = Vert2.GetPosition() - CurrentVertex.GetPosition(); GW_Float a = Edge2.Norm(); Edge2 /= a; GW_Float d1 = Vert1.GetDistance(); GW_Float d2 = Vert2.GetDistance(); /* Set it if you want only to take in acount dead vertex during the update step. */ // #define USING_ONLY_DEAD#ifndef USING_ONLY_DEAD GW_Bool bVert1Usable = Vert1.GetState()!=GW_GeodesicVertex::kFar && Vert1.GetFront()==&CurrentFront; GW_Bool bVert2Usable = Vert2.GetState()!=GW_GeodesicVertex::kFar && Vert2.GetFront()==&CurrentFront; if( !bVert1Usable && bVert2Usable ) { /* only one point is a contributor */ return d2 + a * F;//这里F理解为流速,a理解为Δx } if( bVert1Usable && !bVert2Usable ) { /* only one point is a contributor */ return d1 + b * F; } if( bVert1Usable && bVert2Usable ) {#else GW_Bool bVert1Usable = Vert1.GetState()==GW_GeodesicVertex::kDead && Vert1.GetFront()==&CurrentFront; GW_Bool bVert2Usable = Vert2.GetState()==GW_GeodesicVertex::kDead && Vert2.GetFront()==&CurrentFront; if( !bVert1Usable && bVert2Usable ) { /* only one point is a contributor */ return d2 + a * F; } if( bVert1Usable && !bVert2Usable ) { /* only one point is a contributor */ return d1 + b * F; } if( bVert1Usable && bVert2Usable ) {#endif // USING_ONLY_DEAD GW_Float dot = Edge1*Edge2; /* you can choose wether to use Sethian or my own derivation of the equation. Basicaly, it gives the same answer up to normalization constants */ #define USE_SETHIAN /* first special case for obtuse angles */ if( dot<0 && bUseUnfolding_ ) { GW_Float c, dot1, dot2; GW_GeodesicVertex* pVert = GW_GeodesicMesh::UnfoldTriangle( CurrentFace, CurrentVertex, Vert1, Vert2, c, dot1, dot2 ); if( pVert!=NULL && pVert->GetState()!=GW_GeodesicVertex::kFar ) { GW_Float d3 = pVert->GetDistance(); GW_Float t; // newly computed value /* use the unfolded value */#ifdef USE_SETHIAN t = GW_GeodesicMesh::ComputeUpdate_SethianMethod( d1, d3, c, b, dot1, F ); t = GW_MIN( t, GW_GeodesicMesh::ComputeUpdate_SethianMethod( d3, d2, a, c, dot2, F ) );#else t = GW_GeodesicMesh::ComputeUpdate_MatrixMethod( d1, d3, c, b, dot1, F ); t = GW_MIN( t, GW_GeodesicMesh::ComputeUpdate_MatrixMethod( d3, d2, a, c, dot2, F ) );#endif return t; } }#ifdef USE_SETHIAN return GW_GeodesicMesh::ComputeUpdate_SethianMethod( d1, d2, a, b, dot, F );#else return GW_GeodesicMesh::ComputeUpdate_MatrixMethod( d1, d2, a, b, dot, F );#endif } } return GW_INFINITE;} 下面给出主要代码
%main.m% load the mesh[vertex,faces] = read_mesh('elephant-50kv');% display the mesh%clf;%plot_mesh(vertex, faces);%shading interp;options = [];%Select some starting point and do the propagation.start_points = 20361;%算出距离start_points的距离场[D,S,Q] = perform_fast_marching_mesh(vertex, faces, start_points, options);%Extract some geodesics and display the result.npaths = 30; nverts = size(vertex,2);% select some points that are far enough from the starting point[tmp,I] = sort( D(:) ); I = I(end:-1:1); I = I(1:round(nverts*1));end_points = floor( rand(npaths,1)*(length(I)-1) )+1;end_points = I(end_points);% precompute some usefull information about the meshoptions.v2v = compute_vertex_ring(faces);options.e2f = compute_edge_face_ring(faces);% extract the geodesicsoptions.method = 'continuous';%options.method = 'discrete';options.verb = 0;paths = compute_geodesic_mesh(D,vertex,faces, end_points, options);% displayoptions.colorfx = 'equalize';plot_fast_marching_mesh(vertex,faces, D, paths, options);shading interp; %compute_geodesic_mesh.mfunction [path,vlist,plist] = compute_geodesic_mesh(D, vertex, face, x, options)% compute_geodesic_mesh - extract a discrete geodesic on a mesh%% [path,vlist,plist] = compute_geodesic_mesh(D, vertex, face, x, options);%% D is the set of geodesic distances.%% path is a 3D curve that is the shortest path starting at x.% You can force to use a fully discrete descent using% options.method='discrete'.%% Copyright (c) 2007 Gabriel Peyreoptions.null = 0;verb = getoptions(options, 'verb', 1);if length(x)>1 path = {}; vlist = {}; plist = {}; for i=1:length(x) if length(x)>5 if verb progressbar(i,length(x)); end end [path{i},vlist{i},plist{i}] = compute_geodesic_mesh(D, vertex, face, x(i), options); end return;endmethod = getoptions(options, 'method', 'continuous');[vertex,face] = check_face_vertex(vertex,face);if strcmp(method, 'discrete')%离散方法的路径只能沿mesh的边行径(也就是三角形的边上) if isfield(options, 'v2v') vring = options.v2v; else vring = compute_vertex_ring(face); end % path purely on edges vlist = x;%终点索引 vprev = D(x);%终点的距离 while true%迭代往距离为0的方向找路径 x0 = vlist(end); r = vring{x0}; [v,J] = min(D(r)); x = r(J); if v>=vprev || v==0 break; end vprev = v; vlist(end+1) = x; end path = vertex(:,vlist); plist = vlist*0+1; return;end%%% gradient descent on edges% retrieve adjacency listsm = size(face,2); n = size(vertex,2);% precompute the adjacency datasetsif isfield(options, 'e2f') e2f = options.e2f;else e2f = compute_edge_face_ring(face);endif isfield(options, 'v2v') v2v = options.v2v;else v2v = compute_vertex_ring(face);end% initialize the paths[w,f] = vertex_stepping(face, x, e2f, v2v, D);vlist = [x;w]; plist = [1];Dprev = D(x);while true;%采用连续的方法,可使路径跨过三角形的中间 % current triangle i = vlist(1,end); j = vlist(2,end); k = get_vertex_face(face(:,f),i,j); a = D(i); b = D(j); c = D(k); % adjacent faces f1 = get_face_face(e2f, f, i,k); f2 = get_face_face(e2f, f, j,k); % compute gradient in local coordinates x = plist(end); y = 1-x; gr = [a-c;b-c]; % twist the gradient u = vertex(:,i) - vertex(:,k); v = vertex(:,j) - vertex(:,k); %[u v]可以将barycentric坐标转成三维坐标 A = [u v]; A = (A'*A)^(-1); gr = A*gr;%梯度的解释请看后面的图片 nx = gr(1); ny = gr(2); % compute intersection point etas = -y/ny; etat = -x/nx; s = x + etas*nx; t = y + etat*ny;%s,t的解释请看后面 if etas<0 && s>=0 && s<=1 && f1>0 %%% CASE 1 %%% plist(end+1) = s; vlist(:,end+1) = [i k]; % next face f = f1; elseif etat<0 && t>=0 && t<=1 && f2>0 %%% CASE 2 %%% plist(end+1) = t; vlist(:,end+1) = [j k]; % next face f = f2; else %%% CASE 3 %%% if a<=b z = i; else z = j; end [w,f] = vertex_stepping( face, z, e2f, v2v, D); vlist(:,end+1) = [z w]; plist(end+1) = 1; end Dnew = D(vlist(1,end))*plist(end) + D(vlist(2,end))*(1-plist(end)); if Dnew==0 || (Dprev==Dnew && length(plist)>1) break; end Dprev=Dnew;endv1 = vertex(:,vlist(1,:));v2 = vertex(:,vlist(2,:));path = v1.*repmat(plist, [3 1]) + v2.*repmat(1-plist, [3 1]);%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%function [w,f] = vertex_stepping(face, v, e2f, v2v, D)% adjacent vertex with minimum distance[tmp,I] = min( D(v2v{v}) ); w = v2v{v}(I);f1 = e2f(v,w);f2 = e2f(w,v);if f1<0 f = f2; return;endif f2<0 f = f1; return;endz1 = get_vertex_face(face(:,f1),v,w);z2 = get_vertex_face(face(:,f2),v,w);if D(z1) 下面给出代码中梯度的算法,以及s,t的算法
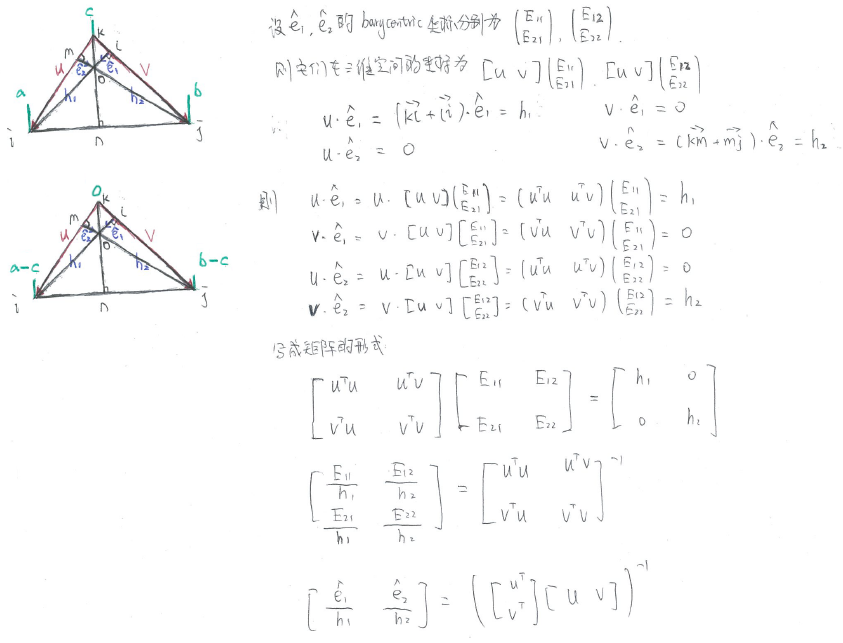
根据梯度的算法(详见:)
就可以得到三角形的梯度为 (a−c)e^1h1+(b−c)e^2h2s,t的算法如下图所示:
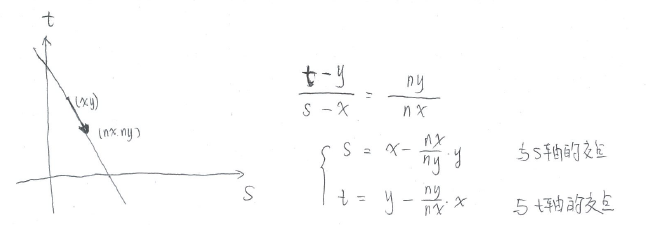
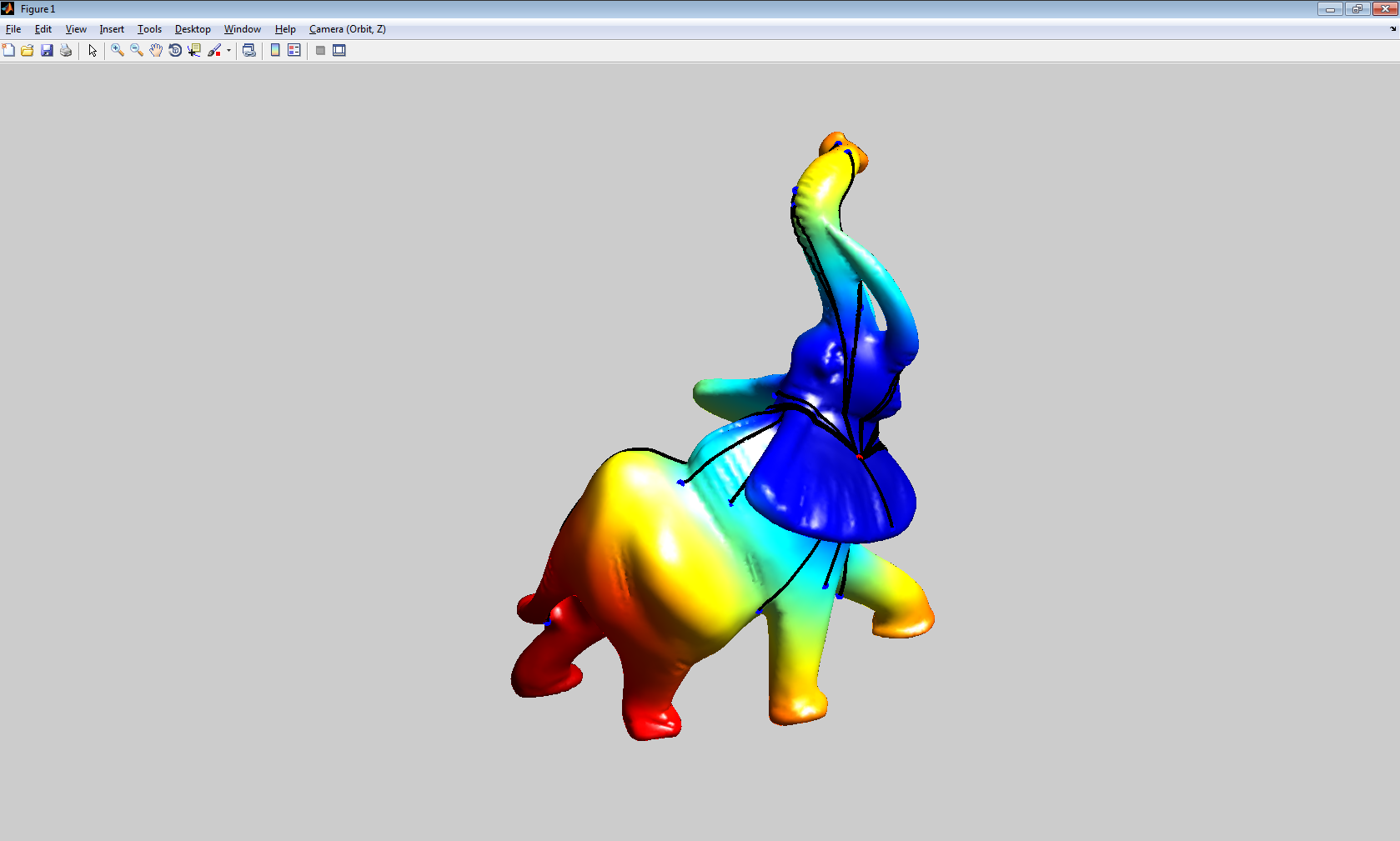
程序运行结果如图:
你可能感兴趣的文章
移动端自动化测试-Windows-Android-Appium环境搭建
查看>>
Xpath使用方法
查看>>
移动端自动化测试-Mac-IOS-Appium环境搭建
查看>>
Selenium之前世今生
查看>>
Selenium-WebDriverApi接口详解
查看>>
Selenium-ActionChains Api接口详解
查看>>
Selenium-Switch与SelectApi接口详解
查看>>
Selenium-Css Selector使用方法
查看>>
Linux常用统计命令之wc
查看>>
测试必会之 Linux 三剑客之 sed
查看>>
Socket请求XML客户端程序
查看>>
Java中数字转大写货币(支持到千亿)
查看>>
Java.nio
查看>>
函数模版类模版和偏特化泛化的总结
查看>>
VMware Workstation Pro虚拟机不可用解决方法
查看>>
最简单的使用redis自带程序实现c程序远程访问redis服务
查看>>
redis学习总结-- 内部数据 字符串 链表 字典 跳跃表
查看>>
iOS 对象序列化与反序列化
查看>>
iOS 序列化与反序列化(runtime) 01
查看>>
iOS AFN 3.0版本前后区别 01
查看>>